
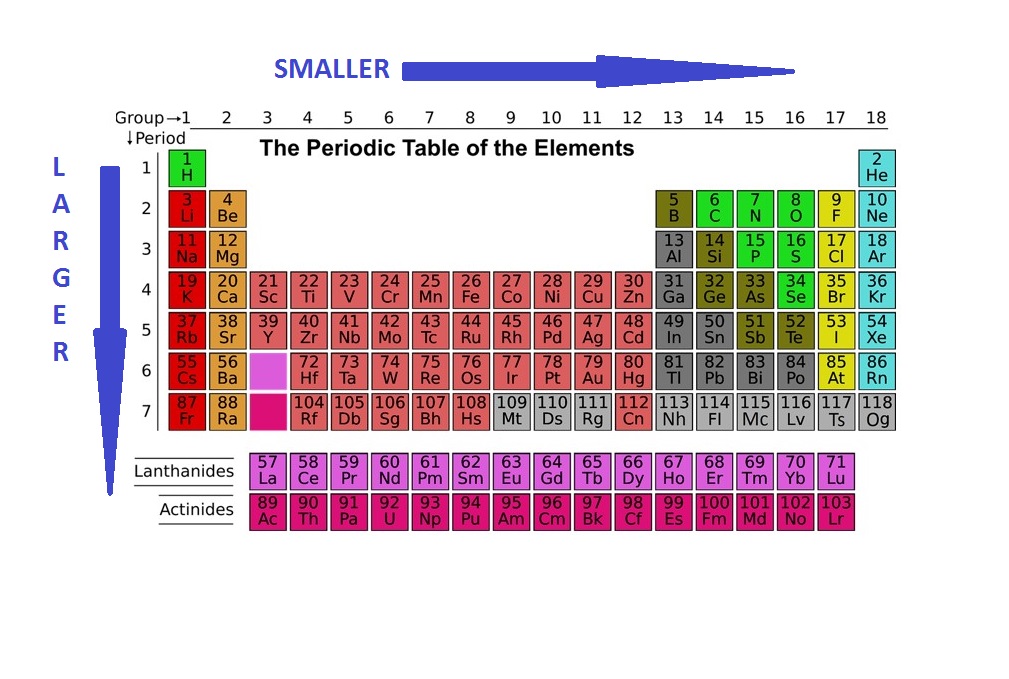
The alkali metals at the extreme left of the periodic table have the largest size in a period.
The C ovalent and Van der Waals radii decrease with an increase in the atomic number as we move from left to right in a period. Variation of Atomic Radii in the Periodic Table Variation Within a Period Read about Metallic and Non-Metallic characters here. The metallic radius of Potassium is 231 pm while its covalent radius is 203 pm. For example, the metallic radius of sodium is 186 pm whereas its covalent radius as determined by its vapor which exists as Na 2 is 154 pm. Thus, a metallic radius is always longer than its covalent radius. In a covalent bond, a pair of electrons is strongly attracted by the nuclei of two atoms. In a metallic lattice, the valence electrons are mobile, therefore, they are only weakly attracted by the metal ions or kernels. It is one half the internuclear distance between the two adjacent metal ions in the metallic lattice. Each kernel is simultaneously attracted by a number of mobile electrons and each mobile electron is attracted by a number of metal ions.įorce of attraction between the mobile electrons and the positive kernels is called the metallic bond. Know about Electron Gain Enthalpy? 3) Metallic RadiusĪ metal lattice or crystal consists of positive kernels or metal ions arranged in a definite pattern in a sea of mobile valence electrons. Therefore, the Van der Waals radius of the chlorine atom is 180 pm. The magnitude of the Van der Waals radius is dependent on the packing of the atoms when the element is in the solid-state.įor example, the internuclear distance between two adjacent chlorine atoms of the two neighboring molecules in the solid-state is 360 pm. It is one half the distance between the nuclei of two identical non-bonded isolated atoms or two adjacent identical atoms belonging to two neighboring molecules of an element in the solid-state. The internuclear distance between two bonded atoms is called the bond length. Therefore, r covalent = ½ (internuclear distance between two bonded atoms). 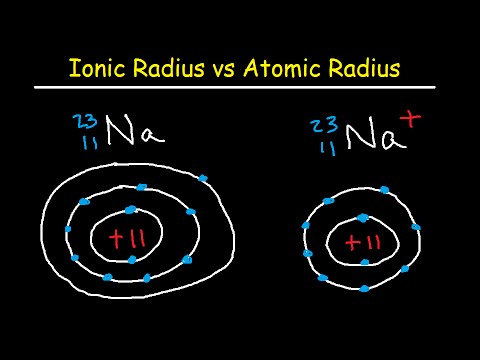
Historical Development of the Periodic TableĬovalent radius is one half the distance between the nuclei of two covalently bonded atoms of the same element in a molecule.Browse more Topics Under Classification Of Elements And Periodicity In Properties

Therefore, we will study these three types of radius because they are vital for a better understanding of the subject. In other words, it is the distance from the center of the nucleus to the point up to which the density of the electron cloud is maximum.Ītomic radii are divided into three types: Atomic radius is the distance from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost shell containing electrons.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
